Your Price for College
- Brian Page

- Jan 18, 2024
- 3 min read
Updated: Jan 22, 2024
Your Kids and College Series: Preparing Your Child to Transition to College
The journey from high school to college is a significant transition for students and their parents. This four-part series focuses on the crucial aspects of guiding your child through this transformative period with trusted resources. The series provides parents with the knowledge and tools necessary to facilitate a smooth and successful transition for their children during this critical time.
Overview
It can be intimidating to see the sticker price displayed prominently by colleges. You get a much more accurate picture of your actual cost after financial aid and scholarships, called the net price. Understanding the various types of financial aid available is crucial for making informed decisions based on your actual college costs.
$55,800 average sticker price for private universities (tuition, room and board, and expenses)
$26,000 average sticker price for public universities (tuition, room and board, and expenses)
As you can see from the data set below, pulled from the National Center for Education and Statistics, private universities' net price (after discounts) is nearly half the original sticker price. It is competitive with the sticker price of public universities.


The lesson is clear:
Never be deterred by the sticker price. Go through the FAFSA and CSS process and apply to private and public universities.
Merit-Based Aid
Think of merit-based aid as a coupon. Many colleges, in particular non state universities, commonly set high sticker prices and use merit aid as a discounting strategy to attract top students and capitalize on the pride parents feel when their child earns a scholarship.
For high achieving students, significant merit aid awarded to students from private universities should be the expectation, not the exception.
A merit-based aid program is designed to attract students with academic excellence, athletic success, artistic achievement, or some combination. Students receive these awards, often through scholarships, regardless of their financial need.
Merit-based aid can be offered by colleges, universities, private organizations, or even government agencies. Students may need to meet specific eligibility criteria, such as maintaining a certain GPA, participating in extracurricular activities, or submitting a portfolio.
Need-Based Aid
Students who demonstrate financial need are eligible for need-based aid. This aid is determined according to the student's and family's financial situation based on income, assets, and family size.
The Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) determines need-based federal aid eligibility. Pell Grants, FSEOGs, and work-study programs are examples of need-based aid.
Student loans
Federal Student Loans
Federal student loans, provided by the U.S. Department of Education, are a common source of financial assistance for college students. These loans come with fixed interest rates and flexible repayment plans. The two main types of federal student loans are subsidized and unsubsidized.
Subsidized loans
Subsidized loans are based on financial need, and the government covers the interest while the borrower is in school or during deferment. There are various types of subsidized loans.
Unsubsidized loans
On the other hand, unsubsidized loans accrue interest from the time the loan is disbursed. There are various types of unsubsidized loans.
Click here to learn more about the specific types of federal student loans.
Private Student Loans
While federal student loans are a common option, they may not cover the full cost of education. Private student loans, offered by banks, credit unions, and other financial institutions, can help bridge the financial gap.
However, unlike federal loans, private loans are credit-based and may have variable interest rates. Private loans may lack the borrower protections and flexible repayment options that federal loans offer.
It's crucial for students to carefully compare interest rates, terms, and conditions before considering private student loans.
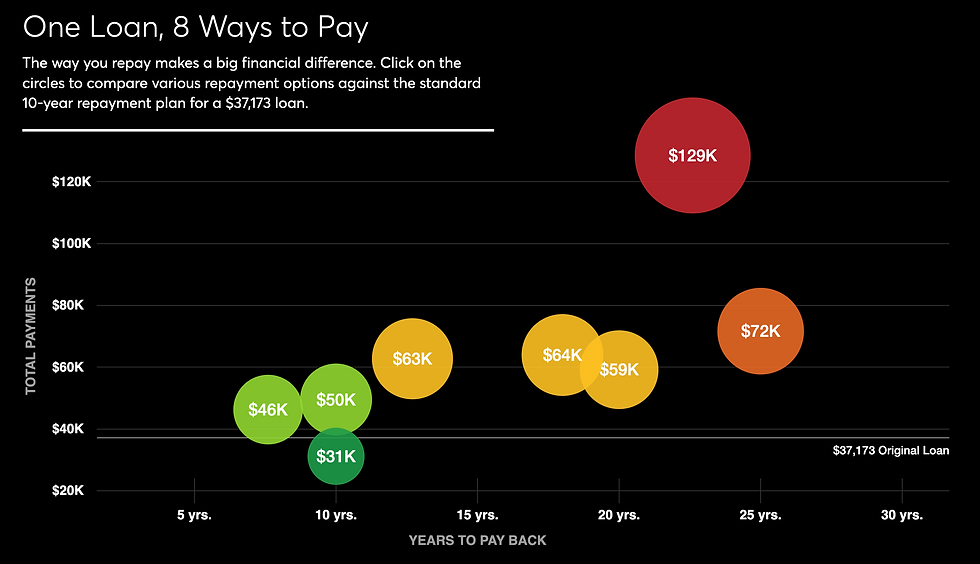
Comparing the Cost of Loans
Click on this interactive (exhibited below) to compare various repayment options against the standard 10-year repayment plan for a $37,173 loan.
Rules of Thumb
Use these three rules of thumb to guide your borrowing decisions for college.
Never borrow more than you expect to earn annually during your first year out of college.
Federal loans are better for borrowers than private loans.
Subsidized federal student loans are better than unsubsidized federal student loans.
FAQs
Student Loan Planner
Student Loan Planner offers tailored consultations to help borrowers achieve long-term financial stability and optimize their repayment journey. In most cases, consultations are offered to individuals who owe significant amounts of student loan debt, typically to graduate schools.
Click here to learn how you can receive consultation to manage existing student loan debt.
Preparing for Academic Success
A course for students ages 13-22 to learn research-backed homework hacks and independent learning strategies. Students work at their own pace in an engaging format. The course is delivered by a team of nationally renowned educators and current college standouts.
Don't miss out on this 57 minute course. Take advantage of the free preview right now!